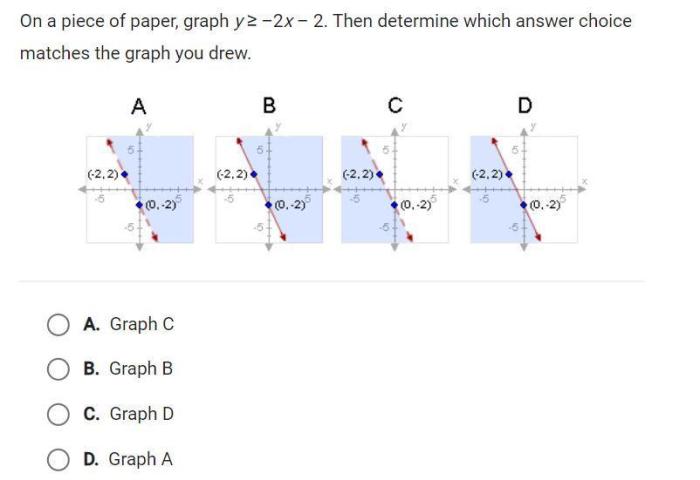
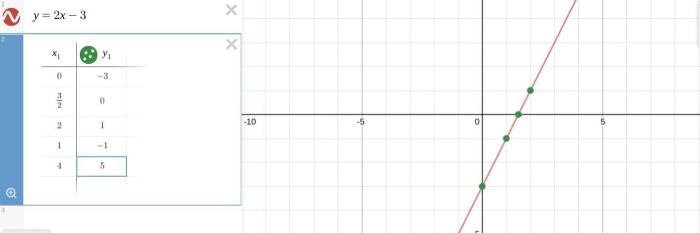
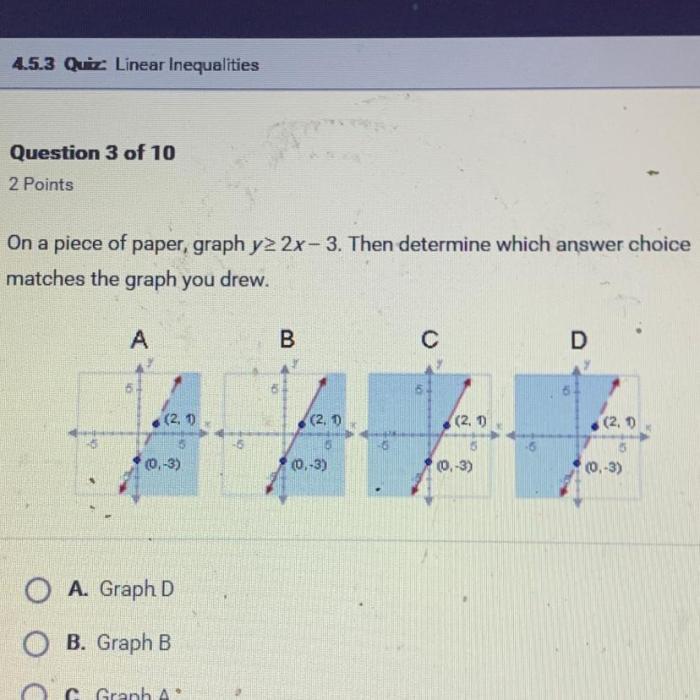
On a piece of paper graph y 2x-3 – The graph of y = 2x – 3 is a fundamental concept in linear algebra that provides a visual representation of the equation. This guide will delve into the intricacies of graphing this equation, exploring its slope-intercept form, plotting techniques, and real-world applications.
Understanding the graph of y = 2x – 3 is essential for students and professionals in various fields, including mathematics, science, and engineering. It empowers individuals to analyze and interpret linear relationships, solve problems, and make predictions based on data.
Linear Equation Interpretation
A linear equation in slope-intercept form is an equation of a straight line that can be written as y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept. The slope represents the steepness of the line, and the y-intercept represents the point where the line crosses the y-axis.
Graphing a Linear Equation
To graph a linear equation, first plot the y-intercept on the y-axis. Then, use the slope to determine other points on the line. For example, if the slope is 2, move up 2 units and over 1 unit to plot another point.
Continue plotting points until you have a line that passes through the y-intercept.
Visualizing the Line
A linear equation represents a set of points that form a straight line. To visualize the line, create a table of values to plot points along the line. Then, draw a line connecting the plotted points. The line represents the solution set of the equation.
Slope-Intercept Form, On a piece of paper graph y 2x-3
The slope-intercept form (y = mx + b) is a convenient way to represent linear equations. The slope (m) indicates the steepness of the line, and the y-intercept (b) indicates the point where the line crosses the y-axis. To write the equation of a line in slope-intercept form, you can use the following formula: y = mx + b, where m is the slope and b is the y-intercept.
Applications of Linear Equations
Linear equations have numerous applications in various fields such as economics, physics, and engineering. For example, in economics, linear equations can be used to model supply and demand relationships. In physics, linear equations can be used to describe the motion of objects.
In engineering, linear equations can be used to design structures and systems.
FAQ Overview: On A Piece Of Paper Graph Y 2x-3
What is the slope of the line y = 2x- 3?
The slope of the line is 2.
What is the y-intercept of the line y = 2x- 3?
The y-intercept of the line is -3.
How do you plot the graph of y = 2x- 3?
To plot the graph, first find the y-intercept by setting x = 0. Then, use the slope to find additional points on the line. Finally, connect the points to form the graph.